 NetSarnag Computer, Inc. offers a product called XManager 3 that will enable a Windows workstation to access a Linux box. However, there are some configuration changes that need to be made on the Linux box for this application to work. The documentation offered by netSarang Computer, Inc. is far from accurate as it looks outdated. Too many assumptions are made. The most blatant assumption is in the versioning of Red Hat. I have learned that Red Hat Enterprise Edition 5 has made changes to the locations of files and file names from earlier versions. After many hours of research, I finally found the proper instructions for Red hat Enterprise Edition 5 users using GDE or KDE.
NetSarnag Computer, Inc. offers a product called XManager 3 that will enable a Windows workstation to access a Linux box. However, there are some configuration changes that need to be made on the Linux box for this application to work. The documentation offered by netSarang Computer, Inc. is far from accurate as it looks outdated. Too many assumptions are made. The most blatant assumption is in the versioning of Red Hat. I have learned that Red Hat Enterprise Edition 5 has made changes to the locations of files and file names from earlier versions. After many hours of research, I finally found the proper instructions for Red hat Enterprise Edition 5 users using GDE or KDE.
How to configure Linux XDMCP GNOME settings for Xmanager
(Successfully tested on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.2 on October 3, 2008.)
To configure Red Hat Linux to use gdm and automatically start the GNOME desktop environment, follow the steps below.
- Edit the /etc/sysconfig/desktop file to define GNOME as the X desktop environment that loads on connection.
-
Open the /etc/sysconfig/desktopfile
-
Locate the DESKTOP= entry.
Note: The entry may need to be created and it is case sensitive.
Change this setting to: DESKTOP=”GNOME” -
Save the file.
-
- Edit the gdm.conffile
-
Open the /etc/gdm/custom.conffile
-
Under the “[xdmcp]” heading, add the Enable entry:
Note: In Red Hat Enterprise Linux version 5: add Enable=true -
Save the file
-
-
Reboot the server (I don’t know if this is necessary, I have grown used to the Windows way of doing things)
After rebooting the Red hat Enterprise Linux server, I launched Xmanager to find that a server has been found.
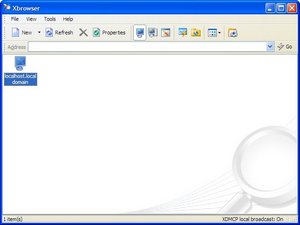
Then clicking on localhost.localdomain resulted in the following screen.
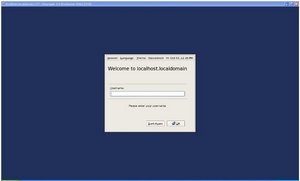
How to configure Linux XDMCP KDE settings for Xmanager
To configure Red Hat Linux to use kdm and automatically start the KDE desktop environment, follow the steps below:
- Edit the /etc/sysconfig/desktop file to define which X desktop environment loads on connection.
- Open the /etc/sysconfig/desktop file
- Locate the DESKTOP= entry.
Note: This entry may need to be created, and it is case sensitive.
For KDE desktop, change this entry to: DESKTOP=”KDE” - Save the file.
- Edit the Xaccess file.
- Open the /usr/share/contig/kdm/Xaccess
- Verify that the following lines appear as shown below:* #any host can get a login window
* CHOOSER BROADCAST #any indirect host can get a chooserNote: The asterisk (*) symbol in front of each line makes the line active. If a pound (#) symbol appears on the line before the * symbol, delete the # symbol. - Save the file.
- Edit the kdmrc file (no change)
- Open the kdmrc file. (Depending on the version of Red Hat, this file may be located under /usr/share/config, /etc/kde/kdm, or /etc/X11/xdm.)
- Under the “[Xdmcp]” heading, change the default entry of Enable=false to Enable=true.
Note: In Red Hat Enterprise Linux version 5, this parameter is set to Enable=true by default. - Save the file.
- Reboot the server (I don’t know if this is necessary, I have grown used to the Windows way of doing things)
Note: As in most documentation that is to be found from all over the internet, there is NO /etc/X11/xdm/xdm-config file to be edited. It only exists in earlier versions of RED hat.
After many hours of searching the search for the source provided below offered the information that I needed and also for the various other versions of Red Hat and details them specifically.