There was a situation where one of the primary domain controllers would not boot and we were forced to upgrade the other domain controller to the primary controller position. This is an AD domain operating on Windows 2003. All references to the failed server were removed from AD. The AD domain seemed to be functioning correctly, until an attempt was made to add another domain controller.
On the attempt, the following error occured:
The operation failed because: This Active Directory installation requires domain configuration changes, but whether these changes have been made on the domain controller server1.mydomain.com is undetermined. The installation process has quit. “The system cannot find the file specified”.
After considerable research, this approach did not result in an error and an additional domain controller was created.
Determine if the existing domain controller has all five FSMOs. The FSMOs are:
- Schema master
- Domain naming master
- RID master
- PDC
- Infrastructure master
To determine this, use netdom, part of the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 Support Tools.
- From the command prompt of the existing domain controller.
- Type netdom query fsmo , then press ENTER.
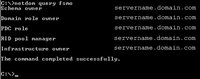
A good result would be The command completed successfully. If any are missing, they will need to be added. For add missing FSMOs, use the Ntdsutil, part of the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 Administration tools Pack.
- From the command prompt.
- Type ntdsutil, then press ENTER
- Type roles, then press ENTER
- Type connections, then press ENTER
- Type connect to server <domaincontroller> , the desired server to connect.
- Type q, then press ENTER
- Type seize <role>
Note: the roles are domain naming master, infrastructure master, PDC, RID master, or schema master.
Note: A popup box will ask if you want to continue with the seize, press Yes. - Continue for each role needed.
Sources: Seizing FSMO Roles, Experts Exchange