Contents
The syslog server comes standard on CentOS/RHEL 7+ and is a system utility providing support for message logging. Support of both internet and unix domain sockets enables this utility to support both local and remote logging. With a couple of configuration changes can become a central monitoring server. There are syntax changes pre CentOS/RHEL 7.4 and CentOS/RHEL 7.4+ for semanage and rsyslog. This article will focus on a working installation for CentOS/RHEL 7.4+.
There are a couple ways of going about this. The /etc/rsyslog.conf can be modified, but it is cleaner to add a new configuration file to /etc/rsyslog.d and that is the approach that will be taken for this article.
Rsyslog Server
Prerequisites
yum update -y yum install policycoreutils-python firewalld rsyslog -y systemctl enable --now firewalld rsyslog
Configuration
Rsyslog syntax has changed where the ~ has been replaced with the word stop. The – minus sign is no longer needed. If your rsyslogd will not start it is likely because you have used ~. Change it to the word stop and restart the service.
This article will focus on udp/514; however, will show tcp/514 configurations too.
Selinux
Since CentOS/RHEL 7.4+, semanage requires the word port.
semanage port -a -t syslogd_port_t -p udp 514 #semanage port -a -t syslogd_port_t -p tcp 514
Firewall Rules
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=514/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=514/udp firewall-cmd --reload
Create Configuration File
There are many possibilities here. This one works for testing purposes and can be modified any number of ways that best fits your given situation.
cat > /etc/rsyslog.d/10-remote.conf << EOF # Provides UDP syslog reception $ModLoad imudp $UDPServerRun 514 $AllowedSender UDP, 192.168.1.0/24 # Provides TCP syslog reception #$ModLoad imtcp #$InputTCPServerRun 514 #$AllowedSender TCP, 192.168.1.0/24 $template RemoteStore, "/var/log/remote/%HOSTNAME%/%timegenerated:1:10:date-rfc3339%" :source, !isequal, "localhost" ?RemoteStore :source, isequal, "last" stop EOF
Restart Service
systemctl restart rsyslog
Validation
Determine if rsyslogd is running and listening.
[root@c7rsyslog ~]# ss -tulpn | grep rsyslog
udp UNCONN 0 0 *:514 *:* users:(("rsyslogd",pid=1572,fd=3))
udp UNCONN 0 0 :::514 :::* users:(("rsyslogd",pid=1572,fd=4))
Rsyslog Client
Create Configuration File
Since the server is using udp/514 there is only one @ preceding the IP address. If there is a tcp/514 connection then use two @@.
echo '*.* @192.168.1.234:514' | tee -a /etc/rsyslog.d/99-rsyslog-client.conf systemctl restart rsyslog
Validation
Determine if the client can access the rsyslogd server.
[root@idm~]# nmap -p 514 -sU -P0 192.168.1.234 Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2019-10-05 09:35 EDT Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.234 Host is up (0.00016s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 514/udp open|filtered syslog MAC Address: 00:0C:29:B2:14:F6 (VMware) Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.35 seconds
A test message may be sent to see if the rsyslog server picked it up.
logger "Test from logclient"
Results
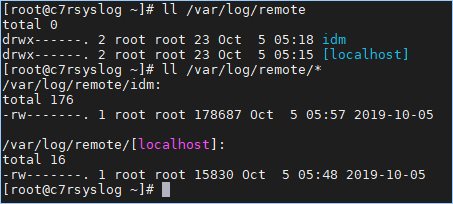
Go back to the server to verify. Note that the serves are listed.
Source(s)
- https://www.tecmint.com/create-centralized-log-server-with-rsyslog-in-centos-7/
- man rsyslogd
- https://linux.die.net/man/8/syslogd_selinux
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/unix_commands/semanage.htm
- https://www.the-art-of-web.com/system/rsyslog-config/
- https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Syslog_config_for_remote_logservers_for_syslog-ng_and_rsyslog_client_server.html